FIT 2.0 released to promote correct insulin injection technique
January 15, 2015 | Thursday | News | By BioSpectrum Bureau
FIT 2.0 released to promote correct insulin injection technique
(Photo Courtesy: www.diyhealth.com)
The event also commemorated the 93rd anniversary of first successful insulin administration on 11th January 1921, at Toronto General Hospital, Canada.
On this occasion, doctors from various hospitals including Bangalore Diabetes Hospital, Apollo Hospital and Advisory Board members of Forum for Injection Technique (FIT) provided tips on overcoming needle phobia for insulin injection dependent patients.
Studies show that more than 80 percent of people have psychological resistance to even initiate an insulin therapy, despite it being indispensable for glycemic control to manage the disease.
As per the new recommendations, special emphasis is to be given to counter allergic reactions arising out of incorrect usage of injections and usage in special groups like pregnant women and people with weak immunity.
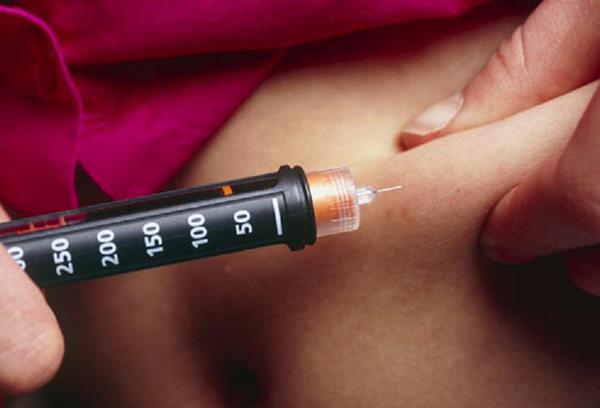
In pregnant women, injections should be given into the abdomen using a raised skin-fold.
In the first trimester women should be reassured that no change in insulin site or technique is needed. In the second trimester lateral parts of the abdomen can be used to inject insulin, staying away from the skin overlying the fetus.
In the third trimester, insulin can be injected over the abdomen while ensuring the skin fold is properly raised. Apprehensive patients may use the thigh or upper arm to inject themselves.
Highlighting on the need to adopt correct injection technique, Dr Prasanna Kumar, senior endocrinologist and CEO, Bangalore Diabetes Hospital said, "Many people are unaware of the complications that may arise due to incorrect insulin administration. People have some favorite injection spots and they use that same spot over and over again. Sadly many people with diabetes haven't received proper education in terms of how to give an insulin shot correctly. If administered incorrectly, lipohypertrophy (LH) is a commonly occurring complication which often causes changes to the skin, and can be disturbing for patients. I appreciate FIT India's efforts to enhance awareness on lipohypertrophy as a complication that is known to be missed, when not diagnosed carefully."
The FIT recommendations also suggest that correct injection technique can help protect against lipohypertrophy, unexplained hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and blood glucose variation.
Shorter needles can provide safety from injecting into muscle, as an insulin injection in the muscle may lead to hypoglycemia.
Several factors including regular inspection of injection sites, preventing reuse of needle, correct site rotation, influence the success of insulin injection therapy.
Dr Anjana Hulse, consultant, pediatric endocrinology, Apollo Hospital, said, "For children with diabetes, insulin injection is the only treatment and they do not have with choice in this regard. It is important to understand where insulin should be injected in the body. But many patients do not understand why this is critical. The recommendations by FIT India have improved the overall acceptance of insulin delivery and injections. FIT2.0 talks about best practices such as using a new needle for every injection, always rotating injection sites and more."
The success of insulin injection therapy and the adherence to it depends on several factors such as a smooth insulin initiation process with counselling that alleviates the fear of needles, the insulin regime, length of needle and the method of administration.
For example, it is always preferable to keep injectable therapy at room temperature, use a new needle for each injection, choose shorter needles with a smaller diameter, and inspect and palpitate the skin prior to each injection to ensure a comfortable injection experience.